1. paging: Introduction
2. TLB
3. Advanced Page Tables
4. Beyond Physical Memory: Mechanisms
5. Beyond Physical Memory: Policies
1. paging: Introduction
Paging을 사용하는 이유
*가변 크기 할당, Segmentation
장점
-sharing, protection support(공유, 보호기능을 제공한다.)
-Address translation, using segment table(segment들이 physical memory의 어디에 올라가는지 확인하기 위해서 segment table을 사용한다.)
단점
메모리 단편화 현상이 발생해, free space가 조각나서 관리된다. 단편화된 메모리는 관리하기 힘들다
*고정 크기 할당, Paging
단편화가 발생하지 않는다. 즉, 외부 단편화라는 복잡한 문제가 발생하지 않는 것이다. 또한 하드웨어적인 지원이 쉽다.
Example of Paging
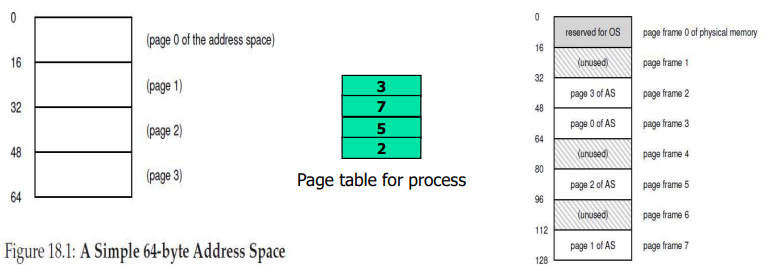
Virtual memory: page라는 고정된 크기의 unit으로 나눠져 있다.
Physical memoy: page frame이라는 고정된 크기의 단위로 나뉘어져 있다.
page table: 어떤 page가 어떤 page frame에 올라가 있는지 mapping해준다. 즉, address translation에 사용되는 것이다.
case1.
Virtual address: 4
4/16=0...4이므로 VPN(virtual page number)는 0이고, page table을 통해 구한 PFN(physical frame number)는 3이다.
physical address: 3*16B+4=52
case2.
Virtual address: 44
44/16=2...12이므로 VPN(virtual page number)는 2이고, page table을 통해 구한 PFN(physical frame number)는 5이다.
physical address: 5*16B+12=92
case3.
Virtual address: 21
21/16=1...5이므로 VPN(virtual page number)는 1이고, page table을 통해 구한 PFN(physical frame number)는 7이다.
physical address: 7*16B+5=117
case4.
Virtual address: 21
bit: 01 0101->VPN은 1이고 PFN은 7이다.
7*16ㅠ+0101=117이다.
Virtual address의 구성요소
page number: page table을 검색할 때 사용
offset: 한 page/frame 내에서 구체적인 주소를 찾아갈 때 사용된다.
page table을 어떻게 관리할 것인가?
page table은 process마다 하나씩 가지고 있고, PCB 내부에 page table도 들어가 있다.→즉, kernel space에 있다. memory에 있다.
page table을 CPU내부에서 관리하면 안되는가?
page table의 크기가 너무 크다.
page table이 메모리에 있기 때문에 여러가지 문제를 야기한다.→시간적인 문제, 성능적인 문제, size 문제(memory에 넣긴 하겠지만 여전히 크기가 크다.)→multi level page table, inverted page table의 해결방법
Page Table이 메모리에 있기 때문에 발생하는 2가지 Issue
1.성능
메모리에 접근하기 위해서 한 번 더 메모리에 접근해야 하는데, 성능저하가 발생한다. 모든 명령어를 실행하기 위해서는 주소변환을 필요로하고, page table은 메모리에 있다.
→성능이 느려지는데, 이를 해결하기 위해서 TLB를 도입
2.page table의 크기가 여전히 크다.
→해결 방법: multi-level page table, inverted page table

P(Present bit): Page가 올라와 있는지 올라와 있지 않는지 표시하는 비트
R/W(Read/Write bit)
U/S(User/Supervisor bit): User mode/Supervisor mode
A(Access bit): 최근에 이 페이지가 사용되었는가?
D(Dirty bit): 이 페이지가 수정되었는지?
Others
V bit(valid bit)
address space가 합법적인지 나타내며, 합법적이지 않다면 segmentation fault가 발생할 수 있다.
fault에는 Page fault와 Segmentation fault가 있다. Segmentation fault는 합법적인 접근이 아니다.
P bitPage fault를 야기시킨다. 합법적인 접근임. 단지 메모리에 올라와있지 않은 것이다.
→Paging은 여러 장점이 있지만, 메모리 접근 횟수가 많아진다.
2. TLB
3. Advanced Page Tables
4. Beyond Physical Memory: Mechanisms
5. Beyond Physical Memory: Policies
'기타 > 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lab3 : [Analyze Ext2 file system internal] (0) | 2022.06.06 |
|---|---|
| [운영체제]Advanced File System (0) | 2022.06.04 |
| [운영체제]Memory Virtualization (0) | 2022.05.23 |
| [운영체제]File System (0) | 2022.05.23 |
| [운영체제]Hard Disk Drives (0) | 2022.05.23 |